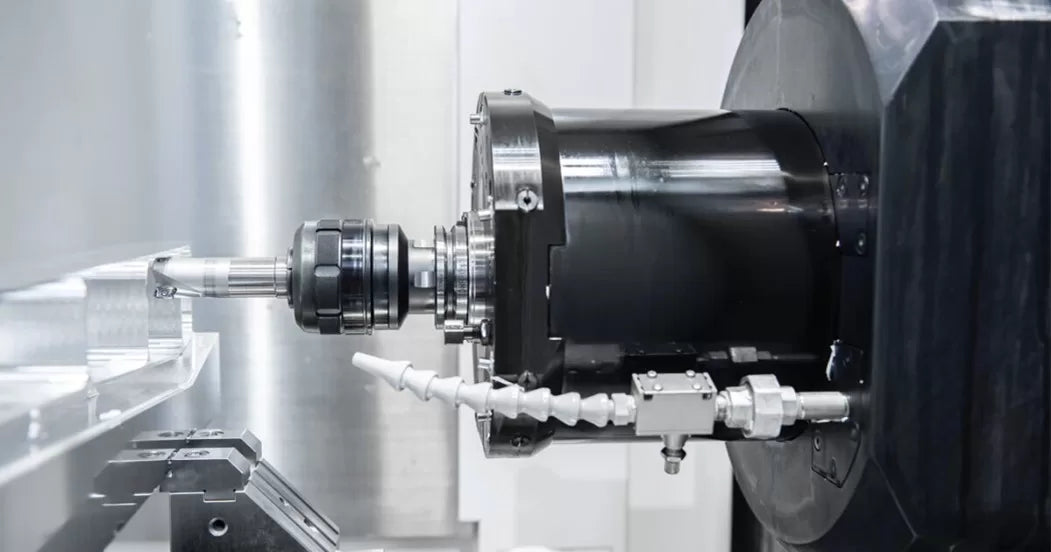

Understanding VMCs, HMCs, and Drill Tapping Centers: A Comparative Guide
In the world of CNC machining, the selection of the right machining center is crucial for achieving optimal results in manufacturing operations. Jaewoo Machines, a leading manufacturer of CNC, VMC, HMC, and DTC machines, understands the importance of choosing the right equipment for specific machining needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the key features, applications, and advantages of Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs), Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs), and Drill Tapping Centers (DTCs), providing valuable insights to help you make informed decisions for your machining requirements.
1. Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs)
Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) are a type of milling machine commonly used in manufacturing and metalworking industries. They are versatile, efficient, and offer precise control over cutting operations. VMCs are widely employed for producing intricate components and prototypes across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
Structure and Operation
VMC machines feature a vertical spindle orientation, where the cutting tool moves in the vertical direction, perpendicular to the workpiece. The workpiece is held stationary on a table that can be moved along the X, Y, and Z axes, allowing for precise positioning and machining. This configuration enables VMCs to perform a wide range of milling, drilling, boring, tapping, and other machining operations with high accuracy.
Advantages of VMC Machines

Versatility: VMCs can perform a wide range of machining operations, including milling, drilling, tapping, and contouring, making them suitable for diverse manufacturing applications.
Precision: With advanced CNC controls and rigid construction, VMCs offer exceptional accuracy and repeatability, ensuring consistent quality in machined components.
Efficiency: Automatic tool changers, high spindle speeds, and rapid traverse rates contribute to faster machining cycles and improved productivity.
Flexibility: VMCs can accommodate various workpiece sizes and materials, allowing manufacturers to adapt to changing production requirements.
Automation Integration: VMCs can be integrated into automated manufacturing systems, enabling lights-out machining for continuous production without human intervention.
Applications
VMC machines find widespread use in industries such as:
Aerospace: Manufacturing aircraft components, engine parts, and structural elements.
Automotive: Producing automotive parts, including engine blocks, transmission components, and chassis.
Electronics: Machining circuit boards, housings, and connectors for electronic devices.
Medical: Fabricating surgical instruments, implants, and medical device components with tight tolerances.
VMC machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, offering versatility, precision, and efficiency in machining operations. Their ability to handle complex geometries and diverse materials makes them indispensable tools for producing high-quality components across various industries.
1. Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs)
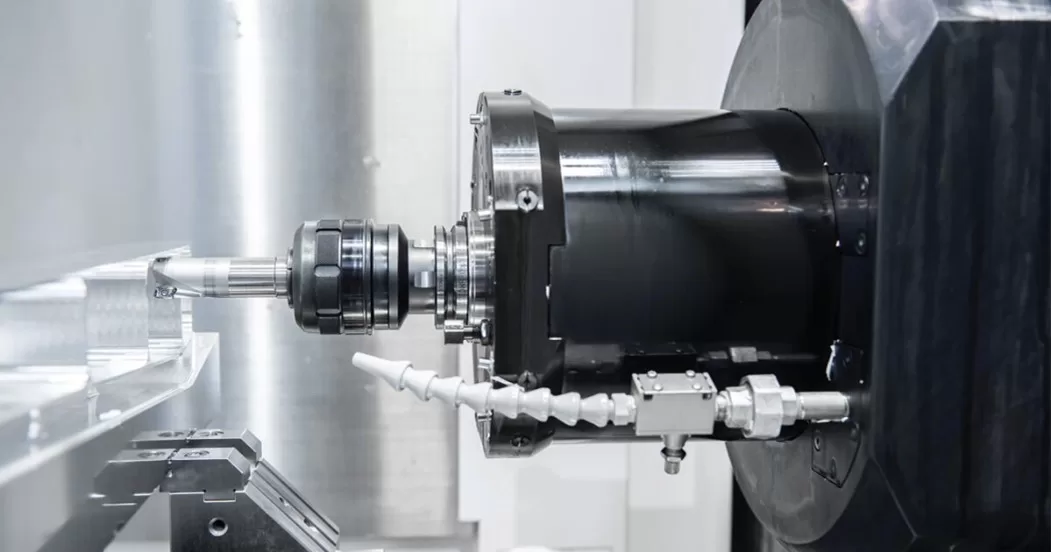

Horizontal Machining Centers, or HMCs, are machining tools characterized by their horizontal spindle orientation. Let’s explore their features and advantages:
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) are a type of machining tool widely used in manufacturing industries for high-precision machining operations. Unlike Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs) where the spindle is oriented vertically, HMCs have a horizontal spindle orientation, which offers unique advantages for certain machining applications.
Structure and Operation
HMCs features a horizontal spindle that holds the cutting tool, which rotates parallel to the workpiece surface. The workpiece is securely held on a horizontal pallet or fixture that can be moved along multiple axes, typically the X, Y, and Z axes. This configuration allows for efficient chip removal and enhances stability during machining operations.
Advantages of HMCs
Better Chip Evacuation: The horizontal spindle orientation of HMCs facilitates efficient chip evacuation, reducing the risk of chip buildup and improving machining performance.
Increased Rigidity: HMCs typically offer greater rigidity and stability compared to VMCs, especially for heavy-duty machining applications, resulting in improved machining accuracy and surface finish.
Enhanced Accessibility: With the workpiece positioned horizontally, operators have easier access to the machining area, simplifying setup, tool changes, and maintenance tasks.
Suitability for Multi-Sided Machining: HMCs is well-suited for multi-sided machining operations, allowing for simultaneous machining of multiple surfaces of the workpiece without repositioning.
Integration with Automation: HMCs can be seamlessly integrated into automated manufacturing systems, enabling continuous production and lights-out machining for increased efficiency.
Applications
HMC machines find widespread use in various industries for machining applications such as:
Automotive: Manufacturing engine blocks, transmission components, and chassis parts.
Aerospace: Producing structural components, wing spars, and landing gear parts.
Die and Mold Making: Machining complex molds and dies with high precision.
Heavy Machinery: Fabricating components for construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial machinery.
Horizontal Machining Centers (HMCs) offer unique advantages for high-precision machining operations, including efficient chip evacuation, increased rigidity, and accessibility. Their versatility and suitability for a wide range of materials make them indispensable tools in modern manufacturing environments.
2. Drill Tapping Centers (DTCs)
Drill Tapping Centers, also known as DTCs, are specialized machining centers designed for drilling, tapping, and hole-making operations. Here are their features and advantages:
Drill Tapping Centers (DTCs) are specialized machining centers designed for precision drilling, tapping, and other secondary operations on workpieces. These machines offer efficient and accurate production of holes and threaded features, making them essential in industries requiring high-speed, high-accuracy drilling and tapping operations.
Structure and Operation
Drill Tapping Centers feature a vertical spindle orientation, similar to Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs), allowing for precise drilling and tapping operations. They are equipped with multiple spindles and tool changers, enabling the machine to perform various operations in a single setup. Additionally, DTCs may have pallet changers or rotary tables to facilitate rapid workpiece indexing and setup changes.
Advantages of Drill Tapping Centers

High Productivity: DTCs offer high-speed drilling and tapping capabilities, resulting in increased productivity and reduced cycle times.
Precision Machining: With advanced control systems and rigid construction, DTCs deliver precise hole positioning, thread accuracy, and surface finish, meeting tight tolerances and quality requirements.
Versatility: DTCs can perform a wide range of operations, including drilling, tapping, boring, reaming, and milling, making them suitable for diverse machining applications.
Reduced Setup Time: The integration of tool changers, pallet changers, and rotary tables enables quick setup changes and efficient production of multiple workpieces with minimal downtime.
Cost Savings: By consolidating multiple machining operations into a single setup, DTCs help reduce labor costs, tooling costs, and overall production expenses.
Applications
Drill Tapping Centers find application in various industries, including:
Automotive: Manufacturing engine blocks, transmission housings, and suspension components.
Aerospace: Producing aircraft structural components, engine parts, and landing gear.
Electronics: Machining housings, enclosures, and heat sinks for electronic devices.
Medical: Fabricating surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and medical device components.
Drill Tapping Centers (DTCs) play a vital role in modern manufacturing, offering high-speed, high-precision machining capabilities for drilling, tapping, and secondary operations. Their versatility, productivity, and accuracy make them indispensable tools in industries requiring efficient production of complex machined components.
Comparative Analysis
Each type of machining center offers unique advantages and applications, catering to different machining requirements. While VMCs excel in versatility and precision for small to medium-sized workpieces, HMCs are preferred for heavy-duty machining and high-volume production. DTCs, on the other hand, specialize in efficient hole-making operations, offering fast and accurate drilling and tapping capabilities.
1. Spindle Orientation
VMCs: Vertical Machining Centers have a vertical spindle orientation, where the cutting tool moves vertically, perpendicular to the workpiece surface.
HMCs: Horizontal Machining Centers feature a horizontal spindle orientation, allowing the cutting tool to move horizontally parallel to the workpiece surface.
DTCs: Drill Tapping Centers typically have a vertical spindle orientation similar to VMCs, as they are primarily used for drilling and tapping operations.
2. Machining Capabilities
VMCs: VMCs excel in performing vertical milling, drilling, boring, and contouring operations on workpieces positioned on a vertically oriented table.
HMCs: HMCs are ideal for horizontal milling, drilling, tapping, and contouring operations, offering advantages in chip evacuation and stability for certain machining applications.
DTCs: Drill Tapping Centers specialize in precision drilling, tapping, and secondary operations, making them suitable for producing holes and threaded features with high accuracy.
3. Workpiece Accessibility
VMCs: VMCs offer easy access to the machining area, allowing for straightforward setup, tool changes, and maintenance tasks due to the vertical spindle orientation.
HMCs: While HMCs provide accessibility similar to VMCs, they may require additional considerations for setup and tool changes due to the horizontal spindle orientation.
DTCs: Drill Tapping Centers offer convenient access to the machining area, facilitating quick setup and tool changes for drilling and tapping operations.
4. Chip Evacuation
VMCs: Chip evacuation in VMCs may require additional measures due to the vertical orientation of the spindle, potentially leading to chip accumulation and tool wear.
HMCs: HMCs have inherent advantages in chip evacuation, as gravity aids in the removal of chips from the machining area, reducing the risk of chip buildup and improving machining performance.
DTCs: Similar to VMCs, DTCs may require attention to chip evacuation, especially during drilling and tapping operations, to prevent chip interference and maintain machining efficiency.
5. Setup Flexibility
VMCs: VMCs offer flexibility in setup for machining operations requiring vertical spindle orientation, accommodating a wide range of workpiece sizes and shapes.
HMCs: HMCs provide versatility for horizontal machining operations, allowing for multi-sided machining and efficient production of components with complex geometries.
DTCs: Drill Tapping Centers offer flexibility for precision drilling and tapping operations, enabling quick setup changes and efficient production of holes and threaded features.
6. Machining Accuracy
VMCs, HMCs, and DTCs: All three types of machining centers are capable of achieving high levels of machining accuracy and surface finish, provided proper setup and tooling are utilized.
7. Application Specificity
VMCs: VMCs are commonly used in industries requiring vertical machining operations, such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
HMCs: HMCs find applications in industries requiring horizontal machining operations, including automotive, aerospace, die and mold making, and heavy machinery.
DTCs: Drill Tapping Centers are specialized machines primarily used for drilling, tapping, and secondary operations in industries such as automotive, electronics, and precision engineering.
8. Automation Integration
VMCs, HMCs, and DTCs: All three types of machining centers can be integrated into automated manufacturing systems, enabling lights-out machining and increased productivity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the features, applications, and advantages of VMCs, HMCs, and DTCs is essential for selecting the right machining center for your specific needs. Whether you require versatility, heavy-duty machining capability, or efficient hole-making operations, Jaewoo Machines offers a range of CNC machining centers to meet your requirements with precision and reliability.
